
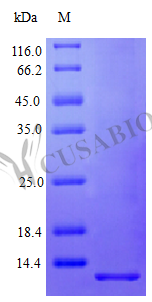
Leitz, A.J., Bayburt, T.H., Barnakov, A.N., Springer, B.A. Nanodiscs unravel the interaction between the SecYEG channel and its cytosolic partner SecA. Nanodiscs in the studies of membrane-bound cytochrome P450 enzymes. Luthra, A., Gregory, M., Grinkova, Y.V., Denisov, I.G. Directed self-assembly of monodisperse phospholipid bilayer nanodiscs with controlled size. The role of membrane properties in Mistic folding and dimerisation. Amphipols, nanodiscs, and fluorinated surfactants: three nonconventional approaches to studying membrane proteins in aqueous solutions. Solubilized (Na+ + K+)-ATPase from shark rectal gland and ox kidney-an inactivation study. Dimer to monomer conversion of the cytochrome b6 f complex. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of membrane-bound pyrophosphatases. Kellosalo, J., Kajander, T., Honkanen, R. Structure of a fluid dioleoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer determined by joint refinement of X-ray and neutron diffraction data. Lipid bilayer composition influences small multidrug transporters. The synergistic action of melittin and phospholipase A2 with lipid membranes: development of linear dichroism for membrane-insertion kinetics. Interaction of membrane proteins and lipids with solubilizing detergents. Membrane proteins, lipids and detergents: not just a soap opera. Computational analysis of membrane proteins: the largest class of drug targets. Together, these methods provide a practical tool kit for those wanting to use SMALPs to study membrane proteins.įilmore, D. coli polar lipid extract (1–2 h) investigate SMALP protein purity by SDS–PAGE analysis and estimate protein concentration (4 h) and detail biophysical methods such as circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy and sedimentation velocity analytical ultracentrifugation (svAUC) to undertake initial structural studies to characterize SMALPs ( ∼2 d). We detail procedures for obtaining 25 g of SMA (4 d) explain the preparation of protein-containing SMALPs using membranes isolated from Escherichia coli (2 d) and control protein-free SMALPS using E. Successful isolation of membrane proteins into SMA lipid particles (SMALPs) allows the proteins to remain with native lipid, surrounded by SMA.

This protocol describes the preparation of styrene maleic acid (SMA) co-polymer to extract membrane proteins from prokaryotic and eukaryotic expression systems. A critical flaw with detergent approaches is the removal of the protein from the native lipid environment required to maintain functionally stable protein. Traditionally achieved with detergents, purification procedures can be costly and time consuming. A significant hurdle is the extraction of the functional protein from its natural lipid membrane. Despite the great importance of membrane proteins, structural and functional studies of these proteins present major challenges.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
